Understanding MAP Enforcement: A Complete Guide for Retailers
Learn how to effectively enforce your MAP policies and protect your brand from violations by sellers with this comprehensive guide for retailers.

Imagine you're shopping online for a new smartphone. You find the same model on several different websites, but the prices are all over the place. This can be confusing and frustrating, right? That's where MAP policies come in.
Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies are rules set by manufacturers that dictate the lowest price at which a product can be advertised. Retailers can sell the product for any price they want, but they can't advertise it below the MAP price. This helps keep the advertised prices consistent across different stores and platforms.
However, just having a MAP policy isn’t enough. It needs to be enforced. Without enforcement, the policy is ineffective, and some sellers might ignore it. Sellers need to see that there are real consequences for breaking the rules, much like how parents enforce rules with their children.
MAP enforcement is especially crucial for brands selling products online. It might seem daunting to monitor and handle every violation, but it doesn’t have to be difficult.
What This Guide Covers:
- What MAP enforcement is
- The benefits of MAP enforcement
- The challenges of MAP enforcement
- How to effectively enforce your MAP policy
What is MAP Enforcement?

MAP, or Minimum Advertised Price, policies are rules set by manufacturers that specify the lowest price monitoring at which a product can be advertised. While retailers can sell the product at any price, they cannot advertise it below the MAP price. This helps maintain the product's value and ensures fair competition among retailers.
MAP enforcement is the process of making sure your sellers follow your MAP policy. Here’s how it works:
- Monitoring: Keep an eye on your sellers to identify any violations of your MAP policy.
- Notification: When a seller violates the policy, notify them about the violation.
- Penalties: Apply penalties as outlined in your MAP policy.
- Termination: If necessary, end your relationship with the non-compliant seller.
Consistently enforcing your MAP policy offers many benefits for your brand, sellers, and customers. However, it also comes with challenges, like monitoring violations around the clock, dealing with legal issues, and enforcing the policy.
But remember, it’s all worth it to maintain the value of your products and ensure fair competition.
The Evolution of MAP Enforcement
MAP policies have evolved significantly over time. Originally, they were developed to combat aggressive price-cutting practices that hurt both profit margins and brand image. Before MAP policies, retailers often reduced prices drastically to attract customers, leading to a race to the bottom. This not only affected profits but also damaged the perceived value of the products.
As online shopping became more widespread, the importance of MAP enforcement grew. The internet made it easier for consumers to compare prices across multiple retailers and for sellers to adjust prices rapidly. This increased the need for strict and effective MAP enforcement to ensure all retailers adhered to the established pricing guidelines.
Benefits of MAP Enforcement Strategies

Why Enforce Your Minimum Advertised Price or MAP Policy?
Without MAP enforcement, your MAP policy is just a document with no real impact. Some sellers might ignore it, leading others to follow suit just to stay competitive, and you won’t see any benefits from having the policy in place. But if you show that MAP violations have real consequences, the benefits are significant.
1. Eliminate MAP Violators and Violations
When you enforce your MAP policy effectively, sellers quickly learn that it's not worth risking a violation. The penalties for breaking the rules outweigh any temporary gains from lower prices. As sellers understand that you are serious about enforcing your policy, violations decrease. Sellers who can’t comply will stop selling your products, and others will avoid risking penalties.
2. Prevent Price Erosion
Price erosion happens when a product’s value drops over time, often due to frequent discounts. Have you ever seen a product heavily discounted and then felt the regular price was too high? That’s price erosion. When one seller lowers their price, others follow, and the new low price becomes the norm, making your regular price seem too high.
By enforcing MAP, you keep your product prices consistent. If your product is never advertised below the MAP, consumers continue to see it as worth its price.
3. Encourage Competition in Other Areas
When price is no longer a factor, sellers compete in other ways, like:
- Offering better return policies and warranties
- Creating more helpful product pages
- Providing more responsive customer service
- Adding perks and incentives
This leads to better overall customer experiences, as sellers strive to stand out in areas other than price.
4. Protect Seller Margins
MAP violations can reduce profit margins for your sellers and you. Gray market sellers, with lower overheads, might sell at much lower prices, driving down margins. High-quality sellers might stop carrying your products if their margins are too low.
Protecting margins ensures that quality sellers continue to sell your products, benefiting both you and your sellers. This also means customers are more likely to have a positive experience with your brand.
5. Maintain Your Brand Integrity
Inconsistent pricing can harm your brand’s image. When customers see widely varying prices, it can be hard for them to tell if they’re buying genuine products or knock-offs. This makes your brand look cheaper than it is.
MAP violations also tend to drive sales to lower-quality sellers who might cut corners on shipping or customer service, leading to negative experiences. These experiences reflect poorly on your brand, as customers associate bad experiences with your products.
Consistent enforcement of MAP helps ensure customers have uniform, positive experiences with your brand.
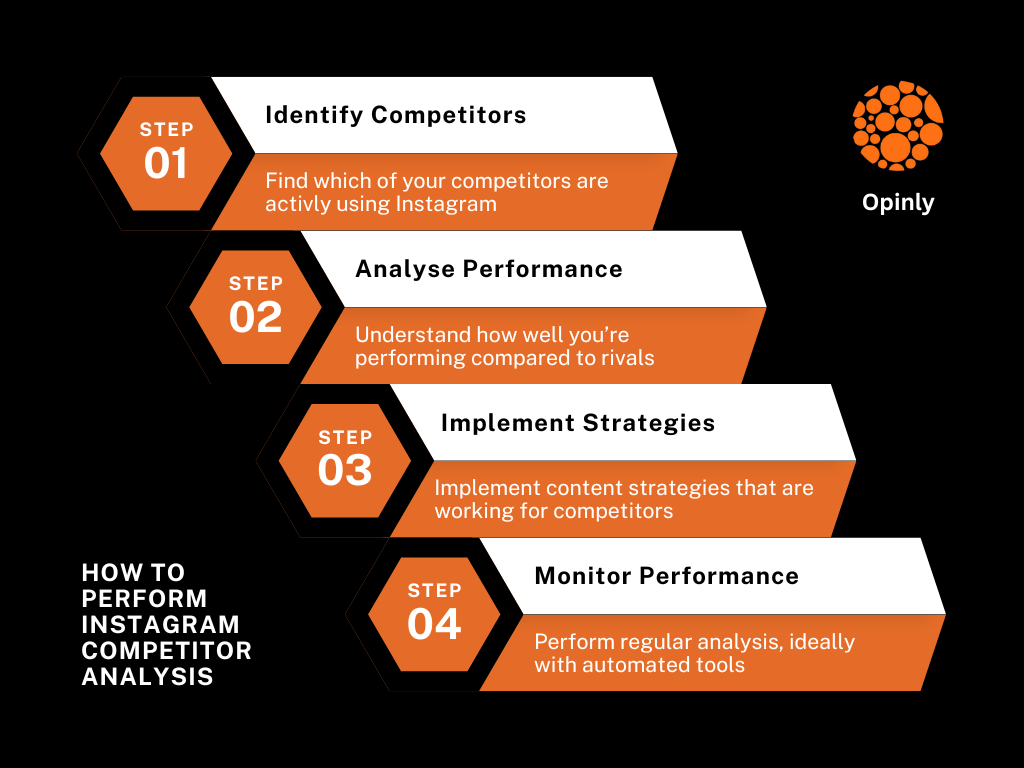
What are The Challenges To Map Enforcement?
Enforcing Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policies isn't as simple as checking product pages occasionally. Without a solid system in place, many brands, regardless of their size, let MAP violations slip through, weakening their MAP policy and missing out on its benefits. Here are some common challenges brands face when enforcing their MAP policy:
1. Scope
Monitoring MAP compliance can feel overwhelming, especially with a large product catalog. The more products (SKUs) you have and the more sellers you deal with, the more sites you need to monitor.
For instance, checking prices on a few products might seem easy until you have to look at those products across hundreds of online stores and marketplaces. For brands with hundreds or thousands of products, manual monitoring becomes impossible.
Additionally, every time you’re not actively checking prices, there’s a chance for violations to go unnoticed. If you only check a website once a week, a seller could violate your MAP policy for six days without you knowing. Advanced tools like repricing software make it easy for sellers to commit short-term violations that you might miss even if you check daily.
This forces brands to decide which products to monitor closely, often leading to inconsistent enforcement and risking the appearance of favoritism.
Solution: Quality MAP monitoring software can help by automatically checking prices for all your products everywhere they’re sold, ensuring your MAP enforcement is thorough and consistent.
2. Consistency
Consistency is important in MAP enforcement. If you don’t treat all sellers the same, you risk showing favoritism and facing potential legal issues.
This challenge extends to how you handle appeals and responses. Whether you’re dealing with the CEO of a major retailer or the owner of a small shop, you must apply your policy equally.
This can be tough if you have personal relationships with some sellers. For example, if a close friend violates your MAP policy, you can't give them special treatment unless you would do the same for every other seller.
Solution: Use templated MAP violation letters to ensure everyone is treated equally and you have a formal, fair process for handling violations.
3. The Gray Market
Gray market sellers are those who acquire your products through unofficial channels — are a significant challenge. These sellers are often hard to contact and can easily ignore violation notices by changing identities frequently.
Marketplaces that host these sellers often don’t provide contact information, making it difficult to enforce your MAP policy. This requires brands to use proprietary seller lists to identify and contact gray market sellers.
Gray market sellers also indicate a leak in your supply chain. If these sellers have your products, someone in your distribution network is supplying them, and you need to address this issue.
Solution: Close the gaps in your supply chain to cut off unauthorized sellers and use specialized tools to identify and contact gray market sellers.
6. Satisfy High-Quality Retailers
Your best retail partners want you to enforce your MAP policy because violations hurt their business too. They can’t compete with low margins and might lose sales to gray market sellers. High-quality retailers want to compete on service and trust you to protect their margins.
By enforcing MAP, you build trust with these retailers, showing that you care about your products, customers, and partners. This makes them more likely to support and promote your brand.
How Do You Enforce MAP Pricing Policy?

Enforcing a Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) policy can be challenging, but it's crucial for protecting your brand and maintaining fair competition. Here’s a simple guide to help you navigate this process:
1. Start with a Strong MAP Policy
Your MAP policy should clearly state the penalties for violations and the steps you will take when a seller breaks the rules. Make sure the policy explains the consequences so sellers understand the risks of violating it. Outline how many “strikes” a seller gets, any situations that lead to immediate termination, and the penalties for each violation.
2. Monitor Sellers Effectively
Manual monitoring is impractical for large catalogs. Use MAP monitoring software to automate the process. Choose a solution that frequently checks prices across various sites to catch violations quickly. Real-time data is ideal.
3. Prepare a MAP Violation Letter
Use template letters for different levels of violations (first strike, second strike, termination). This saves time and ensures consistency. Avoid just sending warning letters. Immediate penalties help reinforce the seriousness of your policy.
4. Handle Appeals and Replies Professionally
Direct any appeals or replies to an antitrust lawyer to avoid legal issues and ensure consistency. Treat all sellers the same, regardless of personal relationships, to maintain fairness and legal compliance.
5. Follow Through with Penalties
Enforce penalties as stated in your policy without leniency. This shows that you are serious and helps deter future violations. Ensure the person in charge of MAP enforcement has the authority to administer penalties.
6. Cut Ties with Problem Sellers
If a seller repeatedly violates your MAP policy, end your relationship with them. This shows other sellers that you take your policy seriously. Maintaining high standards protects your brand in the long run, even if it means losing some sellers.
7. Close the Back Door
If you can't reach a violator directly, find out where they’re getting your products. There might be a leak in your supply chain. Have a conversation with any retail partners who might be selling your products in bulk at discounts. If necessary, cut ties with those who don’t respect your policy.
The Legal Framework of MAP Enforcement

Understanding the Laws and Regulations
MAP (Minimum Advertised Price) policies are governed by various laws and regulations designed to ensure fair competition and prevent anti-competitive practices. Here’s a simple overview of what you need to know:
- Antitrust Laws: In many countries, including the United States, antitrust laws prevent businesses from engaging in practices that restrict competition. This means that while manufacturers can set MAP policies, they must be careful not to violate these laws by fixing prices.
- Resale Price Maintenance (RPM): RPM laws vary by country. In the U.S., manufacturers can suggest prices, but they cannot force retailers to sell at a specific price. MAP policies are allowed because they regulate advertised prices, not actual selling prices.
- Consumer Protection Laws: These laws ensure that consumers are not misled by false advertising. MAP policies help maintain consistent pricing, which supports honest marketing practices.
Differences Between MAP Policies and Other Pricing Strategies

It’s important to understand how MAP policies differ from other common pricing strategies:
- MAP Policies: These set the lowest price at which a product can be advertised. Retailers can sell at any price they choose, but they cannot advertise below the MAP price.
- Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP): This is the price that manufacturers recommend retailers sell their products at. Unlike MAP, MSRP is just a suggestion and not enforceable.
- Unilateral Pricing Policy (UPP): This is when a manufacturer sets a fixed price that all retailers must follow. UPPs are more restrictive than MAP policies and can sometimes be seen as price fixing.
Industries and Products Using MAP Monitoring Policies
MAP policies are commonly used in industries where maintaining a product's perceived value is essential. Here are a few examples:
- Electronics: High-end electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and cameras often have MAP policies to prevent their prices from being driven down.
- Sporting Goods: Brands selling sports equipment and apparel use MAP policies to maintain a premium image and ensure consistent pricing.
- Beauty and Personal Care: Luxury cosmetics and skincare products often have MAP policies to ensure they are not sold at significantly reduced prices, which could diminish their perceived quality.
- Home Appliances: Major appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and vacuum cleaners are sold under MAP policies to keep prices stable and fair across different retailers.
- Toys and Games: Popular toys and games, especially during peak seasons like holidays, often have MAP policies to prevent drastic price reductions.
Conclusion
Enforcing MAP policies is essential for keeping your products' value, ensuring fair competition, and protecting profits. Consistent prices build brand trust and deter bad sellers. It also promotes better practices among your partners.
Implementing and maintaining MAP policies is key to long-term success. Start with a clear policy and use automated tools to monitor prices. Treat all sellers fairly and enforce penalties. Fix supply chain leaks to stop unauthorized sellers.
By doing this, you protect your brand, ensure fair competition, and keep good relationships with your sellers. A well-enforced MAP policy benefits everyone – your brand, your sellers, and your customers.
Take Control of Your Pricing with Opinly AI
Ready to protect your brand, ensure fair competition, and maximize your profits? Opinly AI offers the best competitor price tracking software to help you enforce your MAP policies with ease.
Don’t let MAP violations undermine your brand’s value. Let Opinly AI handle the heavy lifting of price tracking and enforcement. Sign up now and see how our advanced tools can make a difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How Do You Enforce a MAP Policy in Ecommerce?
Enforcing a MAP policy in ecommerce involves monitoring your product prices across various online platforms to ensure compliance. Use automated tools to track prices in real-time and set clear penalties for violations. Consistent enforcement helps maintain fair competition and protects your brand’s value.
2. Why is It Important to Enforce a MAP Policy with Resellers?
Enforcing a MAP policy with resellers ensures that your products are advertised at consistent prices, which protects your brand’s perceived value and prevents price wars. It also ensures that high-quality resellers can maintain healthy profit margins, encouraging them to continue selling your products.
3. What Tools Can Help Enforce Your MAP Policy in Ecommerce?
Automated MAP monitoring tools are essential for enforcing your MAP policy in ecommerce. These tools track product prices across multiple platforms and notify you of any violations in real-time. This allows you to take immediate action and maintain consistent pricing across all channels.
4. What Are the Challenges of Enforcing a MAP Policy for Ecommerce Brands?
The main challenges include the vast scope of monitoring required, ensuring consistent enforcement, dealing with gray market sellers, and navigating legal considerations. Automated tools and clear policies help overcome these challenges by providing consistent monitoring and enforcement.
5. How Can Enforcing a MAP Policy Benefit Ecommerce Resellers?
Enforcing a MAP policy benefits ecommerce resellers by creating a level playing field where they compete based on service and quality rather than price. It helps maintain their profit margins, encourages better business practices, and ensures they continue to have a positive relationship with the brand.